Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) enables your governance, development, and maintenance of Anaplan use cases. You can now work with ALM features in Anaplan’s User Experience (UX) to manage the lifecycle of your pages alongside that of your models.
With the UX, you now build pages inside apps. Apps contain all the different pages users need when analyzing data and planning. Pages connect to models. A page displays data from its source model, but is not a part of the model in the way a dashboard is. Pages do not sync with ALM when you run a model sync.
We’ve developed a roadmap of features to enable you to work with your apps and pages throughout the ALM workflow. Phase one is now complete.
UX ALM paradigm compared to model-sync ALM
ALM for models requires separate models for each lifecycle phase (for example: development, test, and production); changes made in development are promoted through the lifecycle via the model-synchronization functionality.
The vision for UX ALM is to only require a single app to support multiple lifecycle phases. This video visualizes the concept and demonstrates the new functionality:
Note: A single page only displays data from one source model at a time and all the cards on a page display data from the same model. However, the ability to associate multiple models with a page enables you to switch between source models as part of an ALM workflow. When you switch to a new source model, the data that displays on your page and its cards updates.
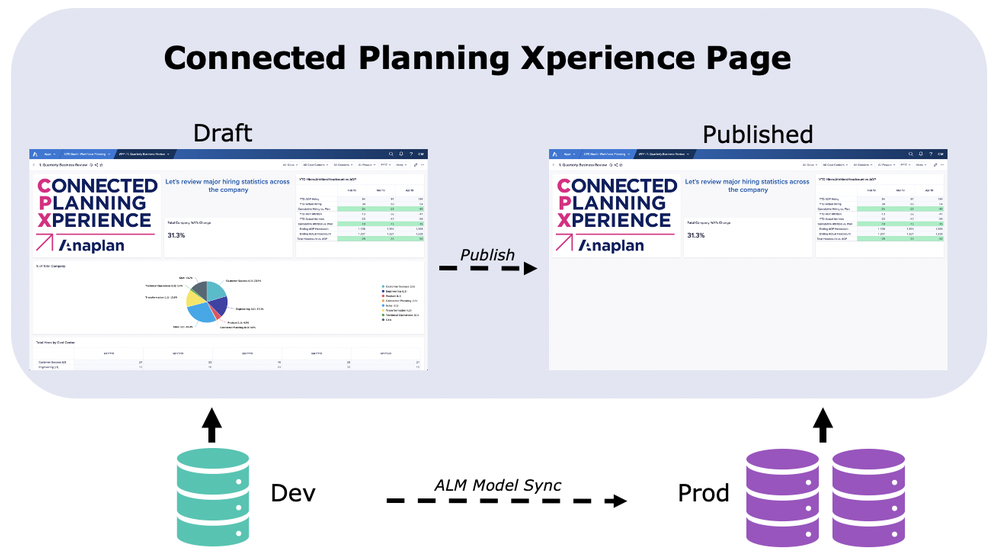
You can make changes to draft pages based on data from your development model, then publish your changes to end users after you synchronize your development and production models
In the visualization below, the Connected Planning Xperience page on the right in production has an image, text, KPI, and grid cards, which is accessible to users of the two associated production models. On the left, the page’s draft state is connected to the development model and has additional chart and grid cards saved ready for publishing after the ALM model sync process.
UX features to use support ALM processes
These features enable ALM processes today:
UX ALM process today
Example use cases supported in phase one
| |
Development and production models
|
Development and many production models |
Development, test, and production models |
| Example |
|
|
|
| Supported? |
Changes can be made against Dev and published against Prod when ready
|
Changes can be made against Dev and published against all Prod models when ready
|
Changes cannot be published to Test without being published to Prod at the same time. The app or page with all draft changes can be duplicated and repointed at Test until this is natively supported.
|
Work with draft pages and production models
This example walks you through the process to create and update pages in an app alongside model synchronization updates.
There are three stages to this process:
-
Create your app and associated models.
-
Make app changes based on the development model.
-
Synchronize and publish your changes.
Create your app and associated models
Create your app with pages and associate the models in your ALM flow with those pages.
In this example, we have one app, two pages, and three models (Dev Model, Prod Model A, and Prod Model B) associated with each page.

Make app changes based on the development model
Create new draft pages and save unpublished changes to pages based on structural changes to the development model (shown in green below). These drafts and unpublished changes are not visible to end users until they are published. It's not necessary to create another app to make changes against the development model before you publish them to end users.
Synchronize and publish
Synchronize model changes from the development model to the production models and then publish new draft pages and unpublished changes in published pages. Once you synchronize your development and production model, end users can use these new app components and changes.
After the ALM model synchronization process, all models are up to date in a new version (v2). The app pages are up to date based on the publish process. Note the middle page is still blue in the diagram below because we did not make any changes to this page.

Work with test models in a development, test, and production workflow
This example describes how the UX ALM functionality can support test models in the lifecycle.
The current UX ALM functionality supports one draft and one published version of a page. It is not yet possible to publish different versions of the page to different associated models (that is Test and Prod).
Example configuration: Consider this configuration where an app with pages is associated with a development and production model.

Make the necessary changes to your app and pages against the Dev model in draft form.

-
Duplicate the app (the draft changes are also duplicated).
-
Once duplicated, update the associated models of the new test app from Dev and Prod to Test.
-
Synchronize changes from the Dev model to the Test model.
-
Publish the draft and unpublished changes made to the pages in the duplicated app.
-
Invite users to test.
Once the page changes are published and the pages have been associated with the Test model, users can be directed at the test app to test the latest changes to the app and model before they are published in the original app.
-
Synchronize model changes to the production model.
-
Publish the page changes in the original app associated with Dev and Prod.
-
Delete the duplicate app.
Contributing author Chris Marriott.