Author: Dave Smith is a Senior Product Manager at Anaplan.
We are thrilled to announce the rollout of On-Demand Calculation in Polaris, a feature that significantly enhances performance and efficiency for our users. On-Demand Calculation is designed to compute values only when they are needed, leading to a more optimized use of resources and faster data processing.
Key benefits
- Reduced latency: Only the necessary cells are recalculated when data changes, which means users experience faster updates and more responsive interactions.
- Lower memory usage: By calculating and storing only the required regions, the memory footprint is significantly reduced. This is especially beneficial for highly-dimensioned line items, where the potential aggregate space is vast.
- Improved performance: On-Demand Calculation ensures that data changes are processed more quickly, as unnecessary recalculations are avoided. This is particularly useful for line items with deep hierarchies and detailed time dimensions.
Real-world example
Consider a line item dimensioned by both Products and Time, where the Products dimension has a deep hierarchy (e.g., multiple levels of product categories) and the Time dimension spans several years with detailed monthly data. Without On-Demand calculation, all aggregates will be calculated at model-open time and on recalculation as below:
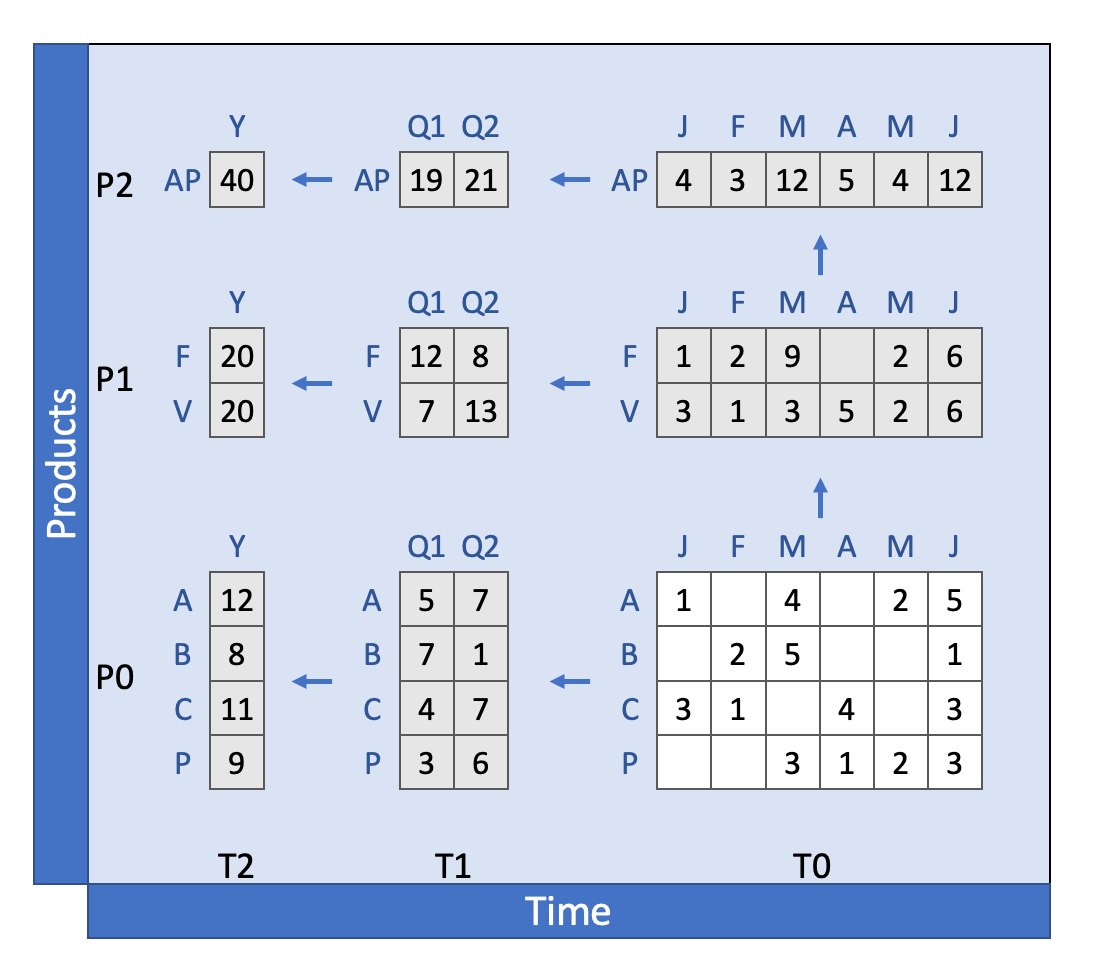
Image: A Line Item dimensioned by Products and Time with all values
calculated.
However, the reality is that in such scenarios, only a small fraction of the total possible cells are typically viewed by users. On-Demand Calculation ensures that only these necessary regions are calculated, reducing memory usage and speeding up data changes:

Image: The Line Item dimensioned by Products and Time whenn a User is looking at the ‘top of the house’ value.
How it works
On-Demand Calculation analyses the model on model-open, and marks certain aggregations for deferred calculation. Currently On-Demand Calculation applies to summary methods where the aggregation is the final step and is not referenced in a further calculation, with the exception of Formula and Ratio summary methods which are never deferred. Rather than calculating these regions up-front as was previously the case, these deferred regions will only be calculated as needed. This not only means that the model opens faster, as less calculation is required immediately, but also that writes to the model are made more quickly, as some recalculation is avoided on write.
As calculations are required on-demand, Polaris keeps the calculated regions in cache to improve the performance of future access. They remain in memory until either the upstream cell data changes, making the region invalid, or the model starts running low on memory and the region has not been accessed for a long time. In both cases, the calculated region is dropped and recalculated only if and when it is needed again for a user view – for example if the aggregation needs to be calculated for an export, or it is viewed in the modelling UX or enterprise UX pages.
Impact on users
- End users: Enjoy faster and more responsive data interactions, with reduced latency on data changes.
- Model builders: May notice fluctuations in memory and populated cell counts, reflecting the dynamic nature of On-Demand Calculation. It will also be important to follow best-practice with regards to testing the model on realistic, scaled data in UAT. However, the overall user experience will be greatly improved, and model open and formula recalculation times will be reduced.
We believe this update will significantly enhance the user experience and look forward to your feedback. Stay tuned for more updates and enhancements from Polaris!
Learn more on Anapedia.
Questions? Leave a comment!